1.2. First Buildbot run with Docker¶
Note
Docker can be tricky to get working correctly if you haven't used it before. If you're having trouble, first determine whether it is a Buildbot issue or a Docker issue by running:
docker run ubuntu:12.04 apt-get update
If that fails, look for help with your Docker install. On the other hand, if that succeeds, then you may have better luck getting help from members of the Buildbot community.
Docker is a tool that makes building and deploying custom environments a breeze. It uses lightweight linux containers (LXC) and performs quickly, making it a great instrument for the testing community. The next section includes a Docker pre-flight check. If it takes more that 3 minutes to get the 'Success' message for you, try the Buildbot pip-based first run instead.
1.2.1. Current Docker dependencies¶
- Linux system, with at least kernel 3.8 and AUFS support. For example, Standard Ubuntu, Debian and Arch systems.
- Packages: lxc, iptables, ca-certificates, and bzip2 packages.
- Local clock on time or slightly in the future for proper SSL communication.
- This tutorial uses docker-compose to run a master, a worker, and a postgresql database server
1.2.2. Installation¶
Use the Docker installation instructions for your operating system.
Test docker is happy in your environment:
sudo docker run -i busybox /bin/echo Success
1.2.3. Building and running Buildbot¶
# Download Buildbot docker-compose.yml.
wget https://raw.github.com/buildbot/buildbot/master/master/contrib/docker/docker-compose.yml
wget https://raw.github.com/buildbot/buildbot/master/master/contrib/docker/db.env
# Build the Buildbot container (it will take a few minutes to download packages)
docker-compose up
You should now be able to go to http://localhost:8010 and see a web page similar to:
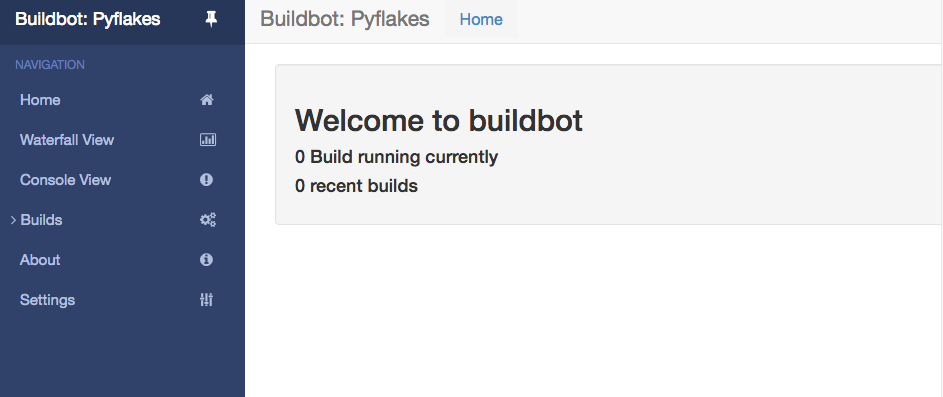
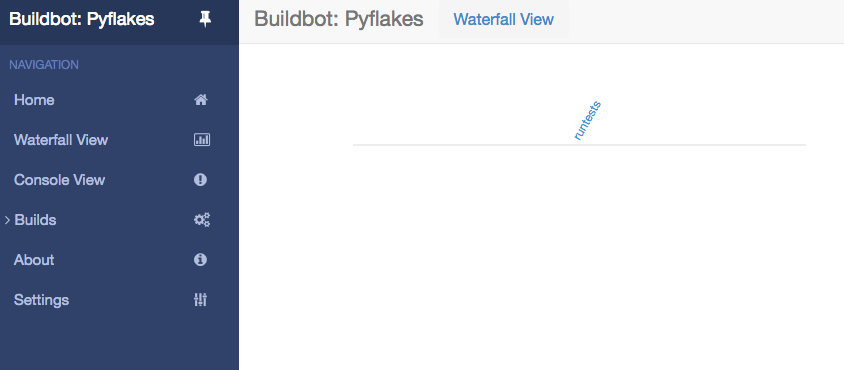
Click on the Waterfall Display link and you get this:
1.2.4. Overview of the docker-compose configuration¶
This docker-compose configuration is made as a basis for what you would put in production
- Separated containers for each component
- A solid database backend with postgresql
- A buildbot master that exposes its configuration to the docker host
- A buildbot worker that can be cloned in order to add additional power
- Containers are linked together so that the only port exposed to external is the web server
- The default master container is based on Alpine linux for minimal footprint
- The default worker container is based on more widely known Ubuntu distribution, as this is the container you want to customize.
1.2.5. Playing with your Buildbot containers¶
If you've come this far, you have a Buildbot environment that you can freely experiment with. The container is storing all its valuable information in /var/lib/buildbot and /var/lib/buildbot_db
You can access your buildbot configuration in /var/lib/buildbot
vi /var/lib/buildbot/master.cfg
1.2.6. Customize your Worker container¶
It is advised to customize you worker container in order to suit your project's build dependencies and need. An example DockerFile is available in the contrib directory of buildbot:
https://github.com/buildbot/buildbot/blob/master/master/contrib/docker/pythonnode_worker/Dockerfile
You've got a taste now, but you're probably curious for more. Let's step it up a little in the second tutorial by changing the configuration and doing an actual build. Continue on to A Quick Tour.
